Oracle Server Architecture
The architecture includes physical components, memory
components and logical structures.
Oracle Primary Architecture Component
Oracle Terms:
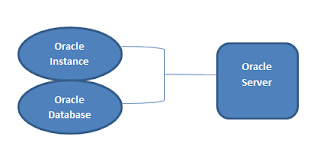
Oracle Server – It is a combination of Oracle Instance and Oracle Database.
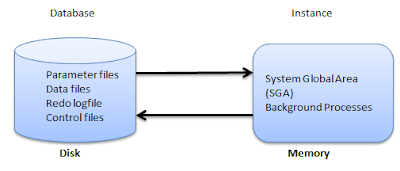
Oracle Database - Oracle database consists of file: datafiles,
control files, redo log files and archive redo log files. The Oracle
server also accesses parameter files and password files.
Oracle Instance - Oracle
Instance consists of two different sets of components:
- Background processes - (PMON, SMON, RECO, DBW0, LGWR, CKPT, D000 and others).
- Memory structures - Comprise the Oracle instance.When an instance starts up, a memory structure called the System Global Area (SGA) is allocated. At this point the background processes also start.
User and server processes – Manage the execution of Sql statements.
- Shared Server Process can share memory and variable processing for multiple user processes.
- Dedicated Server Process manages memory and variables for a single user process.
User - A User is the account you use to connect to a database.
Schema - A Schema is the set of objects (tables, views,
etc.) that belong to that User account.
Tablespace - A tablespace is a storage location where the
actual data underlying database objects can be kept.
Oracle Database
Physical structure
Oracle
Database consists of 3 types of physical files
- Datafiles – These files contain the actual data.
- Redo logfile - Store all changes made to the database as they occur and enable recovery when failures occur.
- Control Files - A small binary file that records the physical structure of the database that includes – database name, locations of associated datafiles and redo files, checkpoint information, current sequence number etc.
Other key files as
noted above include:
- Parameter file – there are two types of parameter files.
- The init.ora file (also called the PFILE) is a static parameter file. It contains parameters that specify how the database instance is to start up.
- The spfile.ora is a dynamic parameter file. It also stores parameters to specify how to startup a database; however, its parameters can be modified while the database is running.
- Password file– specifies which *special* users are authenticated to startup/shut down an Oracle Instance.
- Archived redo log files – are copies of the redo log files and are necessary for recovery in an online, transaction-processing environment in the event of a disk failure.
Memory Structures
The memory structures include three areas of memory:
- System Global Area (SGA) – this is allocated when an Oracle Instance starts up.
- Program Global Area (PGA) – this is allocated when a Server Process starts up.
- User Global Area (UGA) – this is allocated when a user connects to create a session.
Note: A session is a connection
of a user to an instance through a user process.
Processes
Different types of Processes:
- User Process: Starts when a database user requests to connect to an Oracle Server.
- Server Process: Establishes the Connection to an Oracle Instance when a User Process requests connection – makes the connection for the User Process.
- Background Processes: These start when an Oracle Instance is started up.
END OF NOTES
Follow : http://ithelpdeskinc.com/


No comments:
Post a Comment